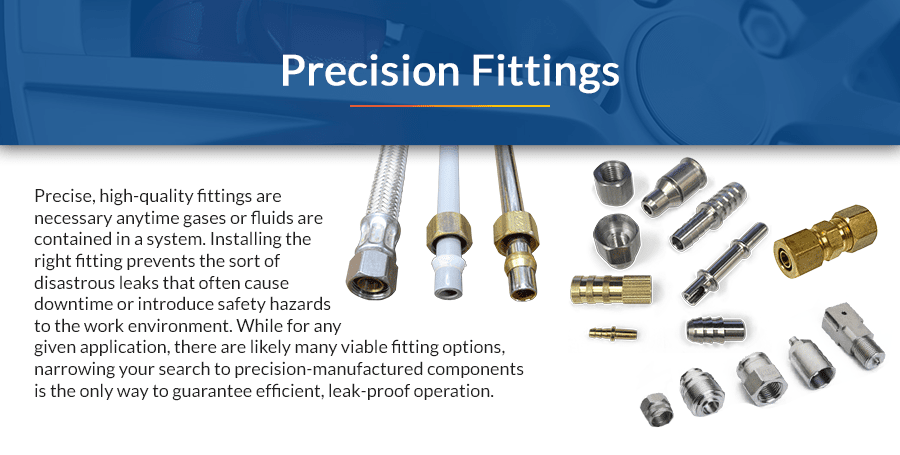
Precise, high-quality fittings are necessary anytime gases or fluids are contained in a system. Installing the right fitting prevents the sort of disastrous leaks that often cause downtime or introduce safety hazards to the work environment. While for any given application, there are likely many viable fitting options, narrowing your search to precision-manufactured components is the only way to guarantee efficient, leak-proof operation.
Precision Fitting Capabilities
Buell Automatics specializes in high-performance fittings designed for maximum durability and efficiency. As experts in precision manufacturing, we produce many fitting types for diverse industrial clients with an emphasis on the following materials and applications:
Brass/Steel/Stainless Steel/Aluminum Fittings
The material selected for fittings is typically selected based on durability, performance, cost, and application. Material selection first must consider what the fitting will come in contact with (water, chemicals, petroleum, air, etc.). If subject to corrosion for example, brass, stainless steel, steel or aluminum may be used with subsequent treatment such as plating, passivation or anodizing. These materials make for the perfect candidate for many fittings. To best serve these diverse clients, we manufacture fittings to varied materials. Some of these fittings are quick disconnect, hydraulic, pneumatic, grease, and plumbing to name a few.
Buell Automatics can support many of the following types of fittings and connectors:
Hydraulic Fittings
Hydraulic fittings form the connections between hoses, pipes, and tubes. These components direct the flow of fluid while also maintaining system pressure and preventing leaks. Depending on the application, materials might include steel, brass, or plastic and often aligns with the material of the system’s conductor. Our precision fittings can accommodate various performance needs, size requirements, and pressure or temperature ratings, being fully customized to each client’s specifications.
Banjo Fittings
Banjo fittings combine a hollow bolt with a spherical fitting to facilitate fluid-transfer. They are most common in brake lines and hoses, but they can be used in other settings that see pressurized fluid transfer. Because of their role in containing hazardous materials, it’s especially important that banjo fittings maintain an airtight seal at all times.
Quick-Connect Fittings
While many fittings are installed once with the intention of remaining in the system long-term, some industrial applications require fittings that can hold up to frequent connections and disconnections. Quick-connect couplings serve this purpose in hydraulic and pneumatic applications. In general, these fittings consist of a simple male-female configuration that can be easily twisted or pulled apart by hand. For quick-connect designs, we balance ease-of-installation with exacting precision standards to ensure that the lines remain fully operational.
Push Fittings
Push fittings, also called push-to-connect fittings, are similar to quick-connect varieties and are also warranted when the system is frequently disconnected. However, rather than requiring two components (male and female), push-to-connect fittings are designed so that tubing can be pushed directly into a hollow fitting.
Vacuum Hose Fittings
Push fittings are commonly seen as the component of choice for vacuum hose applications, so long as the specific fitting has been tested under pressure. Other configurations are possible, but they tend to be permanent and more difficult to install, making push fittings a more convenient option.
Hose Fittings
More broadly, any fitting that connects a hose to another segment of a hydraulic or pneumatic system can be considered a hose fitting. The exact makeup of these components varies drastically with the application: depending on the configuration, hose fittings might be shaped into precise joints or straight connections, fitted exactly to the existing hose. The material must also be compatible with the substance being moved.
Gas or Fuel Line Fittings
Fuel line fittings represent one application where uncompromising precision is vital. Fuel loss is damaging to the operation, the environment, and employee health, so fittings must be carefully engineered to prevent leakage. We offer fuel line fittings to various standard -AN sizes, depending on your desired thread size and application. As a safety precaution, gas fittings are threaded in the opposite direction to most other commercial fittings, preventing accidental connection with lines intended for water or air.
Tube Fittings
Tube fittings resemble hose fittings, and the categories sometimes overlap when a hose is connected to a tube. The difference is that tube fittings are specifically designed to connect rigid spans of tubing to other elements of a system. The shape and material are highly application-dependent, owing partially to the diversity of substances transported in hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
AC Fittings
Air conditioning systems present a relatively volatile environment where pressure and temperature continuously fluctuate. AC units typically contain freon, which poses substantial hazards when released. Due to these factors, AC fittings are designed to be especially resistant to corrosion, pressure, and extreme temperature, all while ensuring an exacting fit with the existing components.
Crimp Fittings
Crimp fittings are designed to fit over tubing before being compressed with crimping pliers or a specialized crimping press. The process of deforming the crimp fitting forms an airtight seal at the end of the length of hose. Because these components must be easily compressible as well as strong and durable, brass is a popular choice, but copper, stainless steel, and poly-alloy fittings are also common.
Threaded Fittings
Perhaps one of the broadest categories, threaded fittings include any connector with interior or exterior screw threads. Certain types of tubing have complementary patterns of threading, providing a simple mechanism for forming a connection. Different variations are possible depending on the needs of the application. For instance, straight threads are designed to connect two components without forming a seal, while tapered threads seal tightly enough to contain pressurized fluid and gas. The latter variety requires skilled, precision manufacturing to prevent leakage.
Adapter/Port Fittings
Adapter fittings—also called standard or union fittings—use straight threads and an O-ring to seal against leakage, which enables highly reliable installation. These fittings connect fuel lines to pumps, regulators, and filters and resist damage from extreme heat and contact with fuel and other chemicals. These are typically made from Stainless Steel in accordance with our customers specifications.
Pipe Fittings
Pipe and Port fittings connect fluid lines to pump ports and regulators for example. The Pipe fitting has a combination of tapered threads to fit into female ports, while the other end can be has straight threads, while Port threads have straight threads on both ends. While tapered threads seal the pipes and lines, these threads present a slightly higher leak risk even when sealed with Teflon tape.
Compression Fittings
Used in plumbing and electrical conduit systems to tubes or thin-walled pipes together. The fittings will be made of one or more compatible materials appropriate for the connection. Compression fittings typically have ferrules in them, and are used for hot and cold water faucets as well as toilet stop valves. These connections are usually used in confined spaces where soldering is difficult.
Flanged Connectors
Bolted flange connectors are suitable for most pressures now in use. The flanges are attached to the piping by welding, brazing, or tapered threads, or by rolling and bending into recesses. Those illustrated are the most common types of flange joints used. The same types of standard fitting shapes-tee, cross, elbow, and so forth-are manufactured for flange joints. Suitable gasket material must be used between the flanges.
Welded Connectors
Welded joints connect the subassemblies of some fluid power systems, especially in high-pressure systems that use pipe for fluid lines. The welding is done according to standard specifications that define the materials and techniques.
Brazed Connectors
Silver-brazed connectors are commonly used for joining nonferrous piping in the pressure and temperature range where their use is practical. Use of this type of connector is limited to installations in which the piping temperature will not exceed 425″F and the pressure in cold lines will not exceed 3,000 psi. Heating the joint with an oxyacetylene torch melts the alloy. This causes the alloy insert to melt and fill the few thousandths of an inch of annular space between the pipe and fitting.
Flared Connectors
Flared connectors are commonly used in fluid power systems containing lines made of tubing. These connectors provide safe, strong, dependable connections without the need for threading, welding, or soldering the tubing. The connector consists of a fitting, a sleeve, and a nut.
Straight Threads vs. Tapered (Pipe) Threads
The threads in straight-threaded fittings run parallel to each other. The shaft of the fitting also stays straight until the end without reducing in diameter or tapering. Fittings with straight threads employ O-rings to create a complete seal. Adapter and port fittings use only straight threads.
In the United States, straight threads must meet American National Standard Straight Pipe Thread (NPS) or American Standard Straight Coupling Pipe Thread (NPSC) standards, depending on the type of pipe and application.
Conversely, tapered threads run along a 2-degree angle. The shaft often tapers to wedge into the fitted surface’s opening. The tension between the shaft, threads, and opposing surface provide a nearly complete seal. Adding Teflon tape makes the seal stronger against potential leaks. Pipe fittings typically only have one end with tapered threads.
In the United States, tapered threads follow American National Standard Taper Pipe Thread standards (NPT).
AN Thread Sizing
Different industry bodies have put forth their own standards for thread sizing, including both the National Pipe Thread (NPT) and British Standard Pipe (BSP) guidelines. We are careful to ensure that all precision fittings align with standard thread sizes to avoid incompatibility.
Army-Navy (AN) sizes are a standard framework for measuring and detailing straight thread sizes. Each number in the scale denotes the size of the outside diameter of a shaft or tube in increments of 1/16 of an inch. Every AN size has a standard thread size. For example, a size 2 tube, according to AN sizing, has a 1/8-inch outside diameter and thread sizes of 5/16-24 SAE. AN sizing continues to size 32, or a 2-inch tube with 2-1/2-12 SAE threads.
NPT sizing, on the other hand, is a scale for tapered threads.
Multi-Spindle Screw Machining
Our ability to craft technical fittings to extremely tight tolerances comes from our use of multi-spindle screw machining. This precision machining process employs a specialized turning drum that rotates spindles horizontally. Each partial rotation brings the spindles to a new subtractive tooling station. The work is divided among these stations such that by the time a full rotation has elapsed, each workpiece has been fully shaped.
In combining multiple spindles and workstations, our screw machining process is incredibly efficient, allowing for series production of orders in excess of 50,000 precision pieces.
Specific multi-spindle screw machine tooling capabilities include:
- Backworking
- Broaching
- Burnishing
- Cross drilling/Tapping
- Cross milling
- Drilling – Standard and High pressure
- Flat generation
- Forming
- Keyway milling
- Reaming
- Shaving
- Sizing
- Slotting
- Stamping
- Tapping
- Thread milling
- Thread rolling
By combining these processes, we can manufacture virtually any kind of precision fitting, including many the varieties discussed above.
CNC Turning
Some fittings are not suited for the multi-spindle screw machine technology. Typically, designs with greater complexity, size and/or lower quantity requirements require different options. To fill the gap, Buell offer CNC turning capabilities to 42mm diameter. These single spindle workhorses offer capabilities to support any of the above fittings when it doesn’t make sense using screw machine technologies.
This precision machining process employs programmable tooling moves in the machine to create most any geometry, feature type or complexity. The precision of well maintained equipment can support tolerances as low as .0005”.
Contact Buell Automatics for Precision Fittings
Buell Automatics is a family-owned precision manufacturing operation that has been in service for over 50 years. In this time, we’ve established ourselves as industry leaders in innovative manufacture techniques, solving cross-disciplinary design challenges for our diverse industrial clients. When you trust Buell Automatics for your precision fittings, you rely on our half-century of service to guarantee the best lead times, prices, and results.
Our team would be happy to discuss the multi-spindle screw machining process or CNC turning in greater depth, answering your questions and determining if our capabilities are the right match for you. To start the conversation about your project, request a quote today.